Whether you were born with a green thumb, inspired by gorgeous greenery-inspired interior designs on social media, or started your plant parent journey during COVID-19, we can all agree that plants are our true friends. They improve our lives by helping reduce our stress levels, allowing us to recover from illness faster, improving indoor air quality, and bringing many other benefits. But sometimes, having one just isn’t enough, or you want to gift your friend a unique plant you have. Sustainable plant propagation might sound daunting and complicated, but we’re here to explain how easily propagating your plants is and how to start.
What is sustainable plant propagation?
Embracing sustainable plant propagation is not just a practice; it’s a commitment to our environment. By growing new plants in a way that conserves resources, minimises water, and respects the ecosystem, we are not only preserving nature but also creating a more beautiful and diverse garden, often in a very affordable way. Propagating plants allows us to multiply our green friends, transforming older plants into multiple younger, smaller, healthier, and more attractive ones.
What to consider when propagating?
- Make sure only to use healthy plants for the source of the propagation
- Pay attention to the growth stage and the right timing for the plant, as well as using the appropriate method
- Give your newly propagated plants extra love and attention, protecting them from heat and drying out
Main Techniques for Plant Propagation
In plant propagation, there are 2 main ways: sexual and asexual propagation.
Sexual propagation involves pollen and egg fertilisation, which leads to seed formation. It’s a simple, effective technique, but it has many disadvantages. This technique can delay flower and fruiting, produce plants that produce seeds that cannot be propagated by this method, and produce identical plants that cannot be reproduced.
Due to these disadvantages, asexual methods of propagation are more commonly utilised by culturists and hobbyists. Asexual propagation involves using leaves, stems, and roots to clone your plants, producing identical plants to the parent plant.
There are 4 main methods for asexual propagation: cutting, division, grafting, and budding.
In this post, we’ll explain the 2 simplest propagation methods you should know to turn your house into a proper green forest.
Cutting
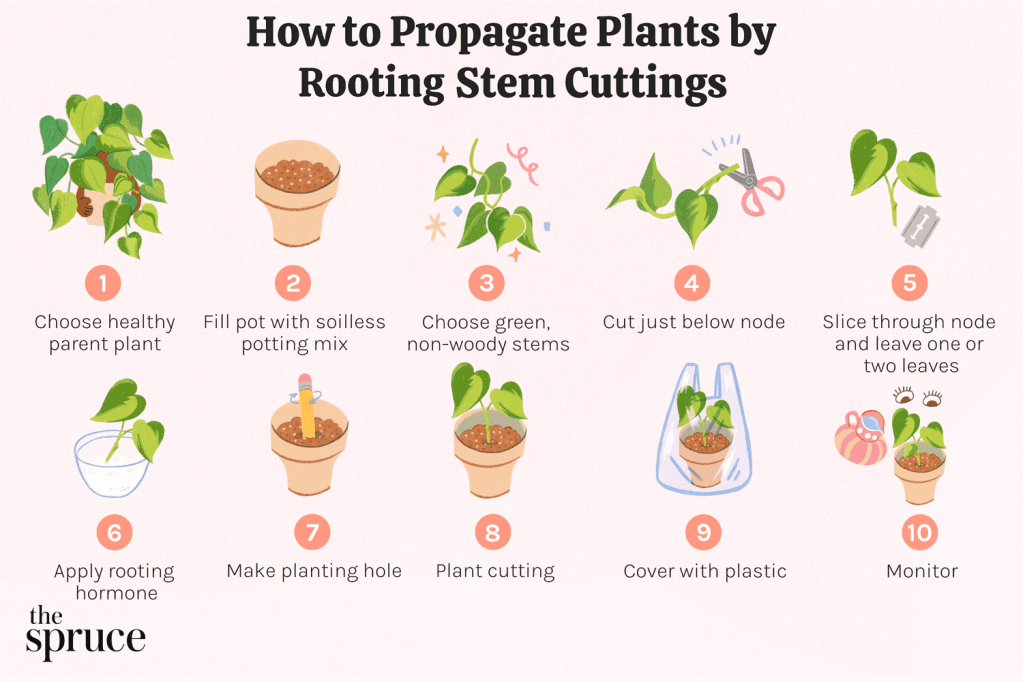
This method involves cutting the vegetative part of the plant (leaf, stem, or root) and then replanting it in a different pot to generate a new plant. This is the best method for beginners as it is relatively quick, affordable, and straightforward.
If using part of the steam, cut it just below a bud (where a leaf attaches to the steam) using a sharp knife or a pruner. Remove any lower leaves that will be buried below the surface, leaving a couple on the top and the flowers, if any. Make a hole bigger than the stem in a potting mix, and place the cutting in the moist soil. Firm the soil around the cutting and water it sparingly. For better results and to maintain humidity and moisture, place the pot inside an inflated plastic bag and seal it with a knot. You can also use a bell jar or any jar upside down. Check how the plant grows and then select which stem-cutting method is the most appropriate for it.
Division
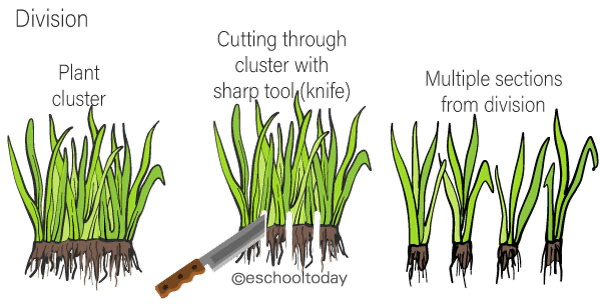
This method creates genetic clones of the parent plant by separating them into smaller pieces. It is important to note that not all houseplants can be grown through division. However, plants that are very large or have offsets crowding the current pot are great candidates for propagation by division. To utilise this method, remove the plant from its pot, lay it with the root ball on its side and use your hands or a knife to loosen the roots, separating them into smaller pieces. Replant the now separated plant in a second pot with fresh potting soil and place plants in indirect light.


Leave a reply to 4 Easy Foods To Regrow From Kitchen Scraps – House Thirty Cancel reply